Choosing the Optimal Sensor – Eddy Current, Magnetic, or Optical?
Eddy Current, Magnetic or Optical – which is the optimal sensor type selection for turbocharger rotational speed measurement?
Despite the push for electrification, the total market for turbochargers accounted for $34.6 billion of revenue in 2023, with a CAGR of 7.11%. Which means that for the foreseeable future turbochargers are going to feature prominently in petrol and diesel powertrain development. One of the critical variables that requires measurement is the rotational speed of the turbocharger compressor wheel, which has a critical impact on exhaust gas temperatures and overall turbocharger reliability.
Advantages of Eddy Current Sensors
For this application there is typically a choice between eddy current sensors, optical sensors or magnetic sensors. A significant advantage of eddy current sensors is their non-contact nature. Optical sensors can be affected by dirt, dust, or misalignment of light paths, whereas eddy current sensors operate without direct contact with the target, making them less susceptible to contamination or physical wear. This ensures consistent performance over time, even in harsh or dirty environments.
Additionally, eddy current sensors are highly resistant to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, electromagnetic interference, and vibrations. Magnetic sensors, while robust, can be influenced by nearby ferrous materials or external magnetic fields, which can distort measurements. Optical sensors, on the other hand, require a clear line of sight and performance can degrade with changes in ambient light or surface reflectivity.
Eddy current sensors also offer exceptional resolution and accuracy, making them ideal for detecting small changes in position, such as those found in rotational measurements. They can measure both displacement and rotational speed with high precision, even at high rotational speeds, making them indispensable in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Introducing ATI’s PICOTURN Turbocharger Speed Sensors
Which is why Accurate Technologies Inc. (ATI) offers the PICOTURN range of turbocharger rotational speed sensors. The PICOTURN system has proven to be a rugged, reliable, simple, accurate and cost-effective solution. The system’s functional principle is a 1MHz pulse induction eddy current design, using a compressor mounted solenoid sensor that detects and counts compressor vanes individually, generating a standard TTL/CMOS output signal.
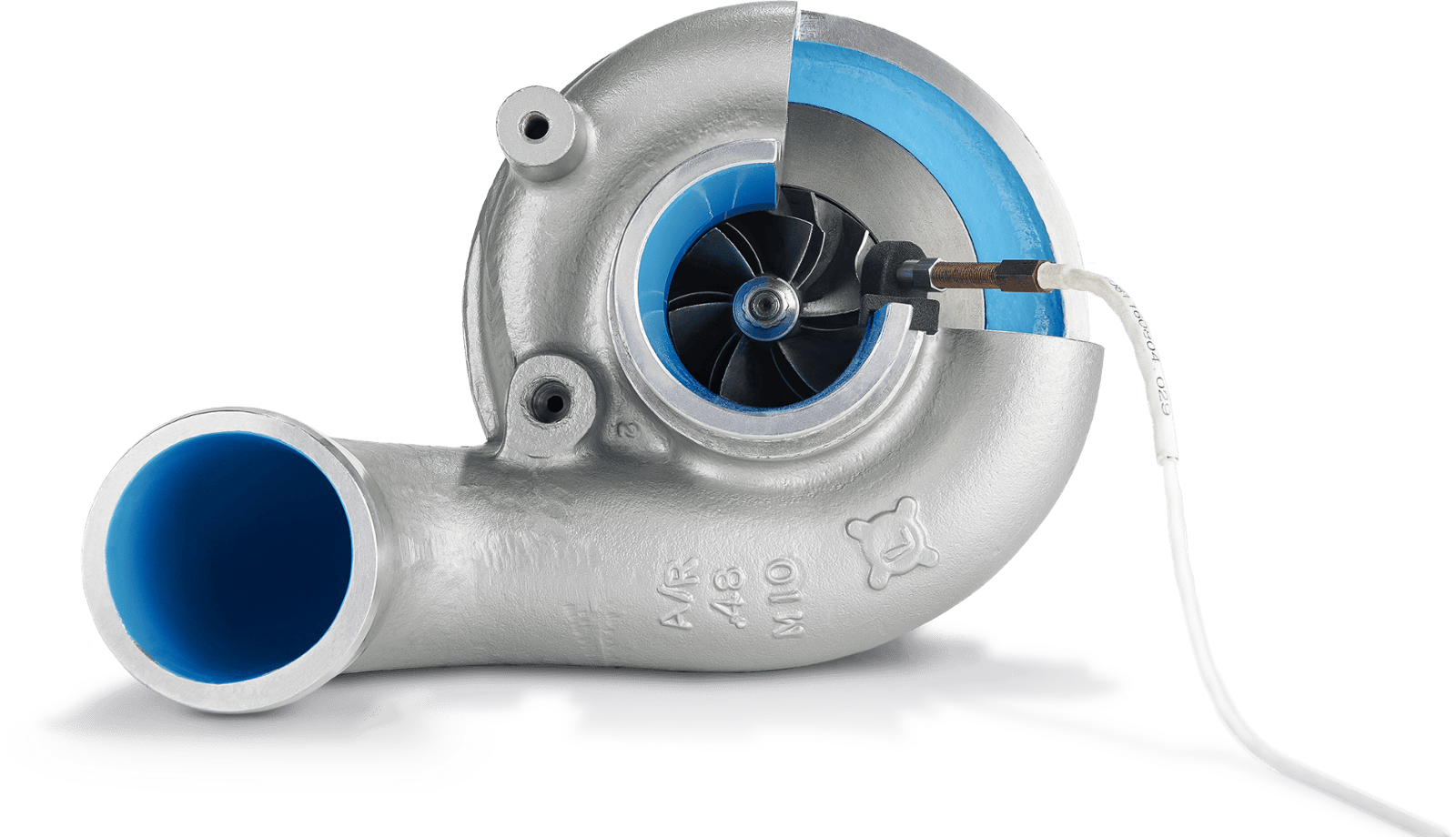
With the inherent advantages of the eddy current technology, PICOTURN turbospeed sensors are capable of accurate compressor wheel speed measurement from just 200 rpm right up to 400,000 rpm.
The PICOTURN system benefits from the high sensitivity of its eddy current design, allowing a large distance between sensor and the rotating turbocharger compressor vanes in the range of 1 mm at 0.6 mm vane thickness. Various PICOTURN sensors are available to accommodate numerous compressor housing user cases, differentiated by the length and thread of the sensor head. The PICOTURN PTSM-H series benefits from enhanced sensitivity, enabling use with titanium compressor wheels and other critical applications where higher temperatures are a priority, exploiting the inherent advantages of the eddy current technology to the full.



