In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive and industrial engineering, achieving optimal performance, efficiency, and compliance with stringent emissions regulations requires precise engine calibration. Traditional calibration methods, which rely heavily on extensive experimental testing and manual fine-tuning, can be time-consuming and costly. Enter Model-Based Calibration (MBC)—a powerful, data-driven approach that revolutionizes the calibration process by leveraging mathematical models and simulation techniques.
What is Model-Based Calibration?
Key Components of Model-Based Calibration
- Data Collection and Experimentation
MBC starts with the collection of experimental data from physical systems. This data is used to create models that capture the relationships between various engine parameters, such as fuel injection timing, air-fuel ratio, and ignition timing. - Modeling and Meta-Model Creation
Using statistical and machine learning techniques, engineers develop mathematical models that predict system behavior. Common methods include polynomial regression, Gaussian processes, and neural networks. - Optimization and Simulation
With the models in place, calibration engineers use optimization algorithms to determine the best parameter settings for achieving objectives such as fuel efficiency, power output, and emissions control. Simulations allow for extensive testing of different calibration strategies before implementing them in real-world applications. - Implementation and Validation
Once an optimal calibration strategy is identified, it is applied to the actual system. Engineers validate the model’s predictions by running real-world tests and refining the model as necessary.
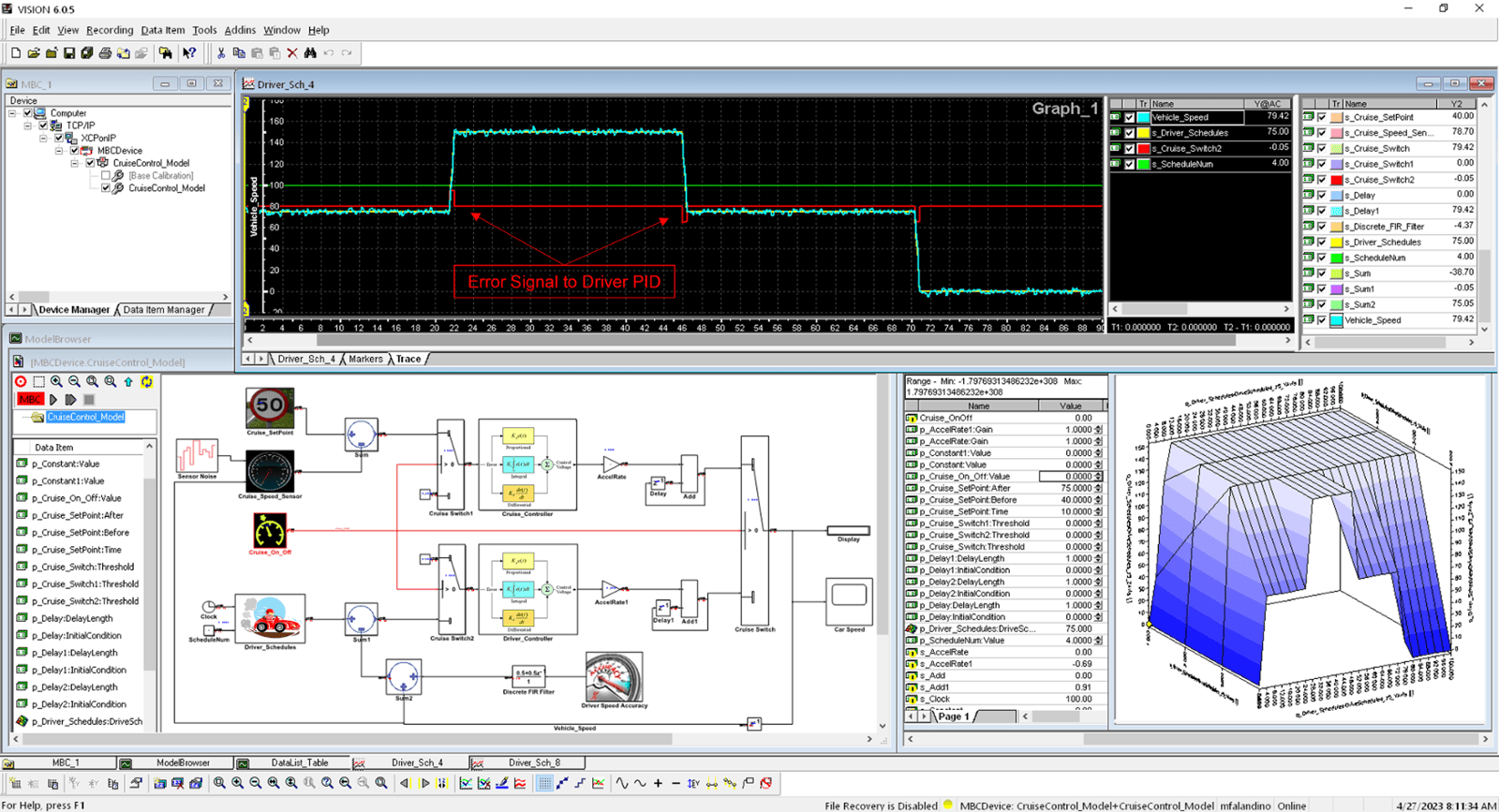
Once an optimal calibration strategy is identified, it is applied to the actual system. Engineers validate the model’s predictions by running real-world tests and refining the model as necessary.
- Reduced Development Time: By minimizing the need for physical testing, MBC significantly shortens the calibration process.
- Cost Efficiency: Decreases reliance on expensive prototype testing and reduces fuel and labor costs.
- Improved Accuracy: Advanced modeling techniques enhance precision in calibration.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that engines meet emissions and performance standards effectively.
- Scalability: Can be applied across various automotive and industrial applications, from combustion engines to electric powertrains.
Applications of Model-Based Calibration
MBC has found applications in the automotive industry for engine calibration, hybrid vehicle powertrain optimization, and emissions control. Beyond automotive applications, MBC plays a critical role in the aerospace industry, energy systems, and industrial automation.
Conclusion
As industries strive for better efficiency and regulatory compliance, Model-Based Calibration has emerged as a potentially game-changing approach that can replace manual calibrator tuning with intelligent, data-driven optimization. By integrating MBC into the calibration workflow, engineers can enhance performance, reduce costs, and accelerate product development, paving the way for smarter, more efficient systems in the future.



